Dna Methylation And Disease
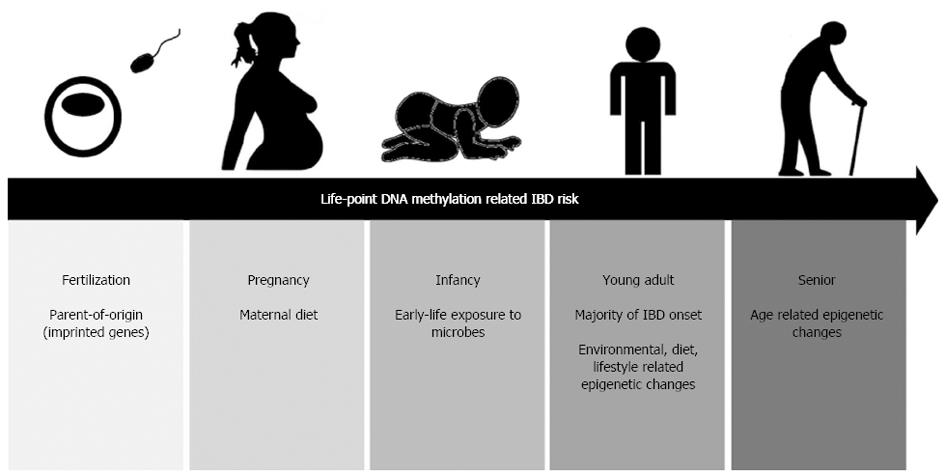
Dna methylation and disease. DNA methylation is of paramount importance for mammalian embryonic development. Aberrations in the DNA methylation system have an important role in human disease. The significance of DNA methylation in shaping the phenotype of the heart remains only partially known.
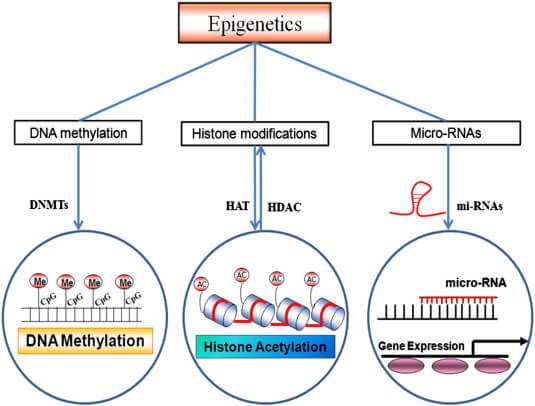
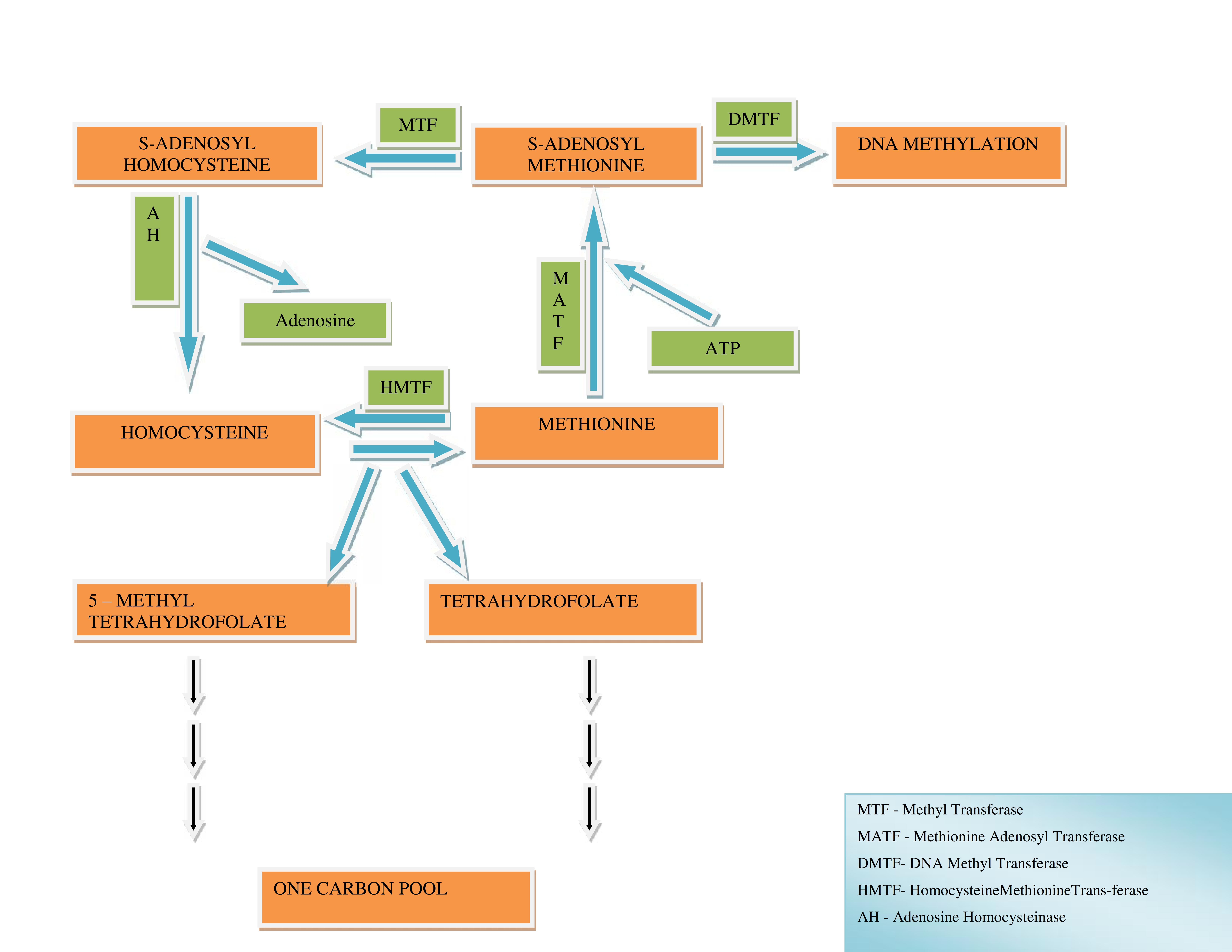
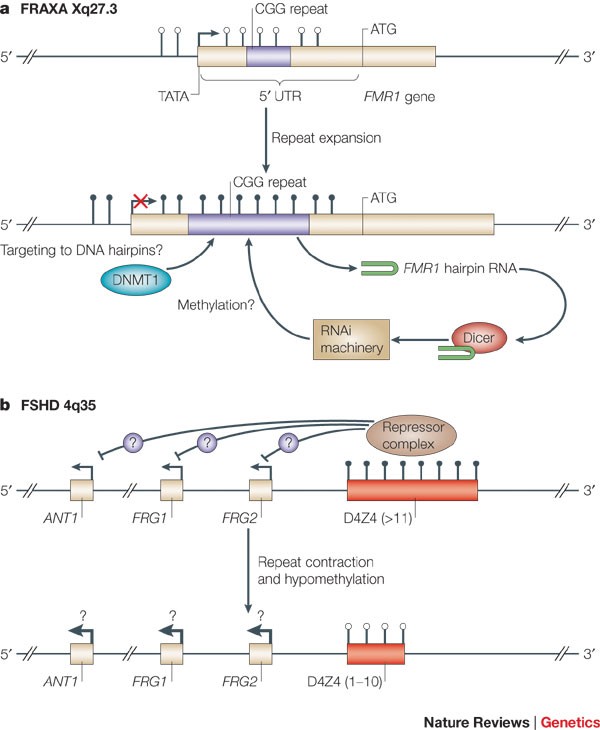
DNA methylation has recently moved to centre stage in the aetiology of human neurodevelopmental syndromes such as the fragile X ICF and Rett syndromes. DNA methylation present in gene promoters gene bodies and repeated sequences has different effects. DNA methylation and human disease.
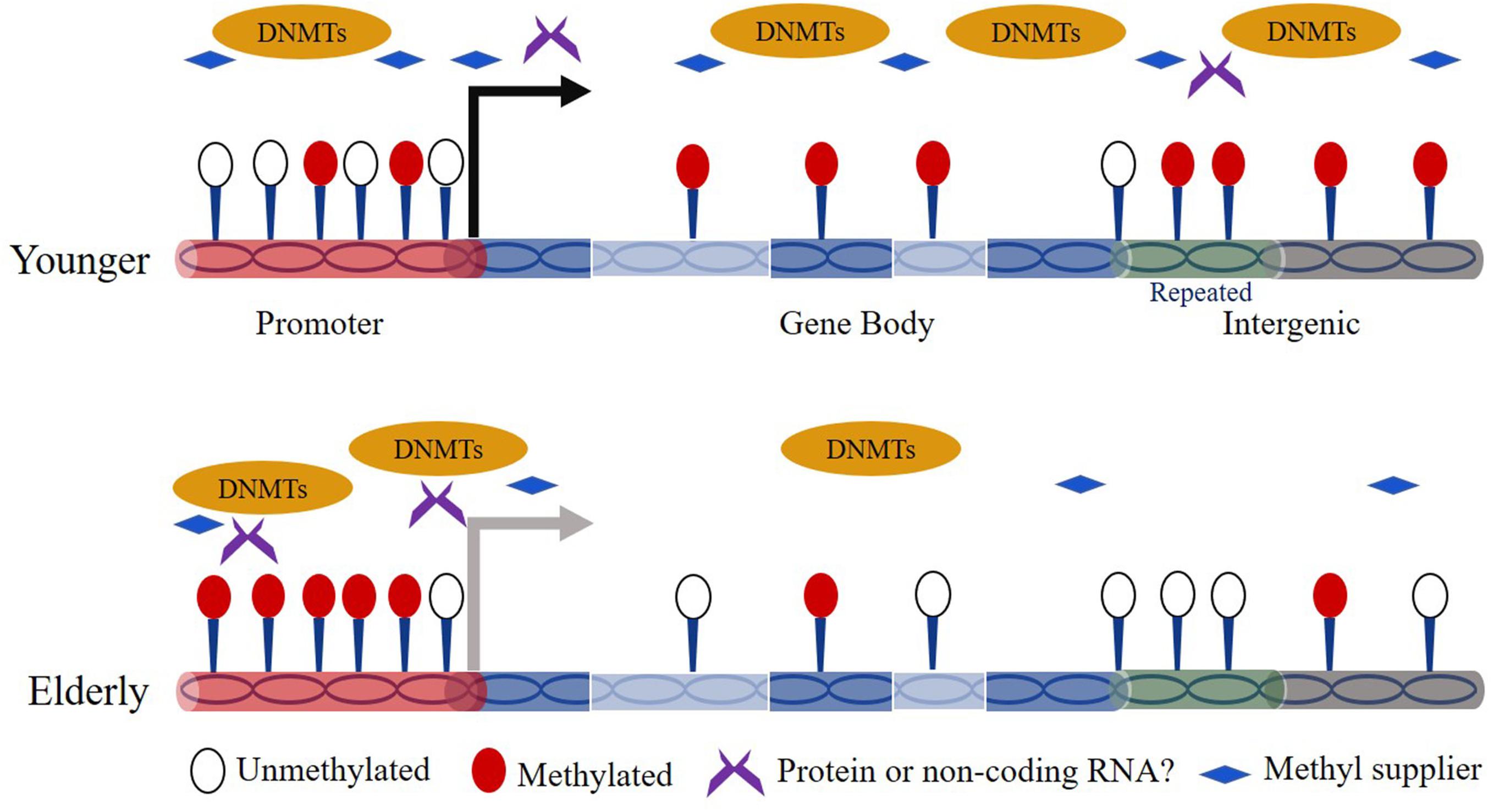
Four independent latent factors 9 19 21only in womenand 27 driven by DNA methylation were associated with cardiovascular disease independently of classical risk factors and cell-type counts. To improve DNA methylation. DNA methylation is a complex process that could hold major clues to health and aging but many more large-scale human studies are needed to fully understand its effects.
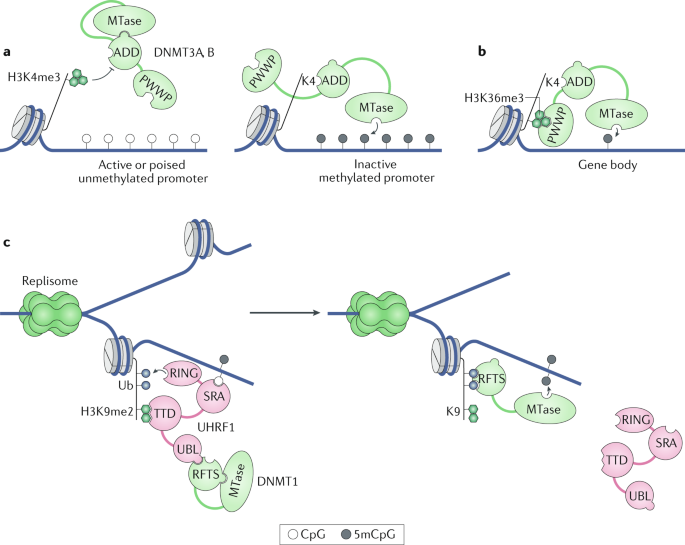
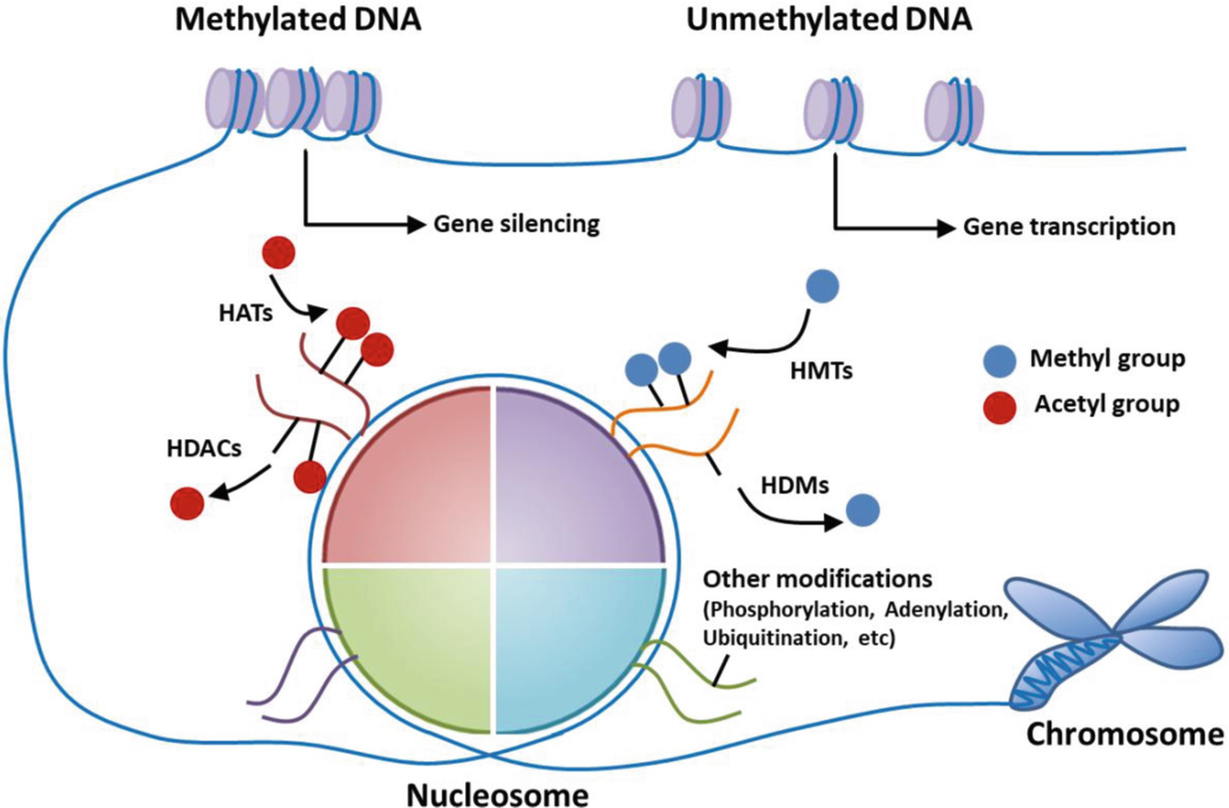
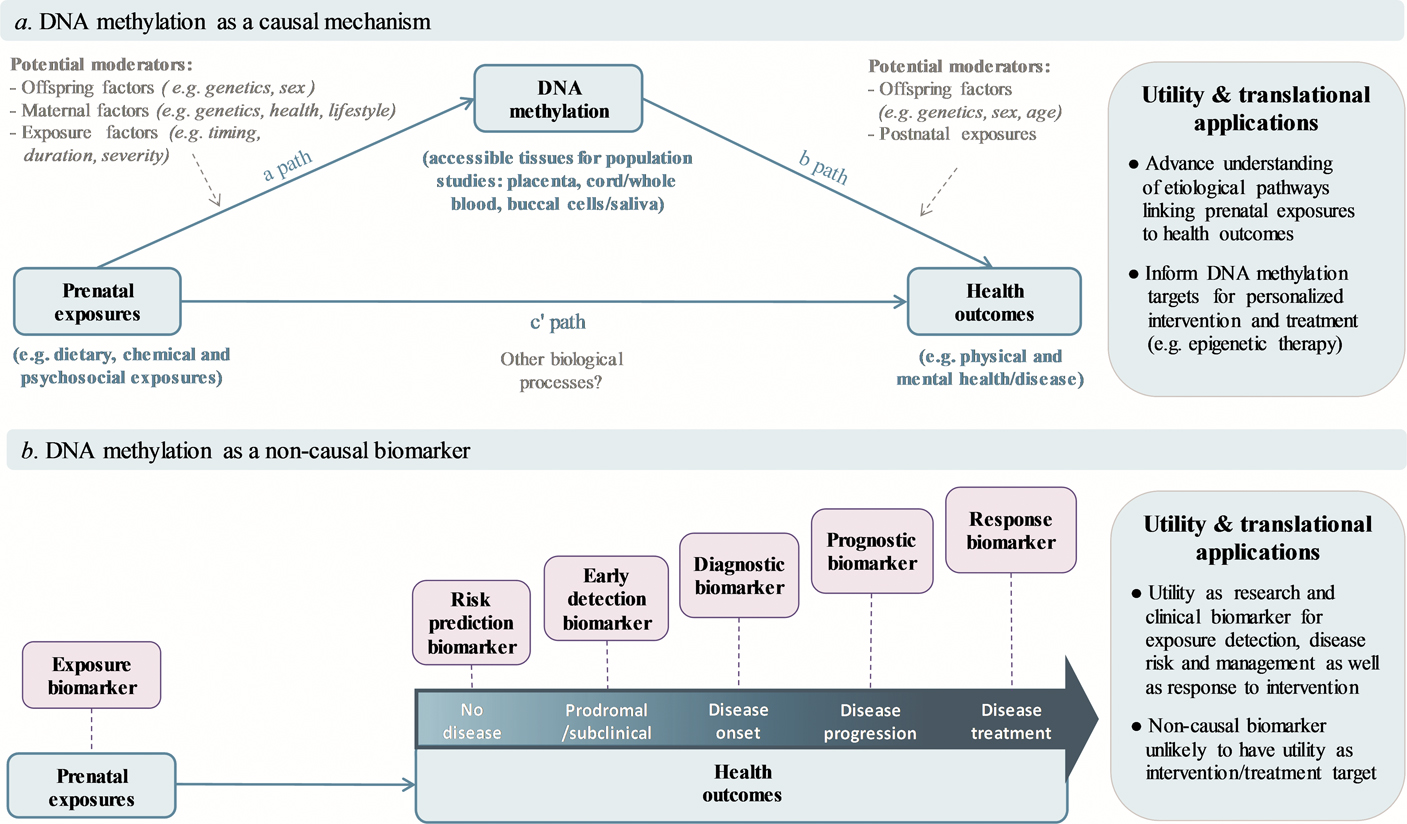
Epigenetic epidemiology enables researchers to explore critical links between genomic coding modifiable exposures and manifestation of disease phenotype. The figure depicts the molecular mechanism linking DNA methylation and inactive transcription. In this review I discuss DNA hypermethylation in disease and its interrelationships with normal development as well as proposed mechanisms for the origin of and pathogenic consequences of disease-associated hypermethylation.
Dynamic DNA methylation orchestrates cardiomyocyte development maturation and disease. In this review we provide an overview of DNA methylation in inflammatory skin diseases with an emphasis on psoriasis and atopic dermatitis. By inhibiting DNA methylation in a mouse model for intestinal tumors for example it is possible to dramatically decrease the occurrence of adenomas 119 and the same is true for other cancer.
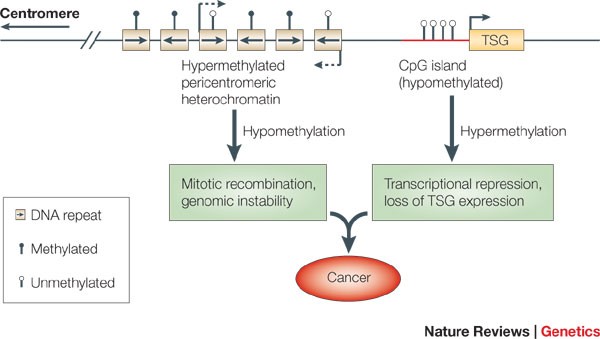
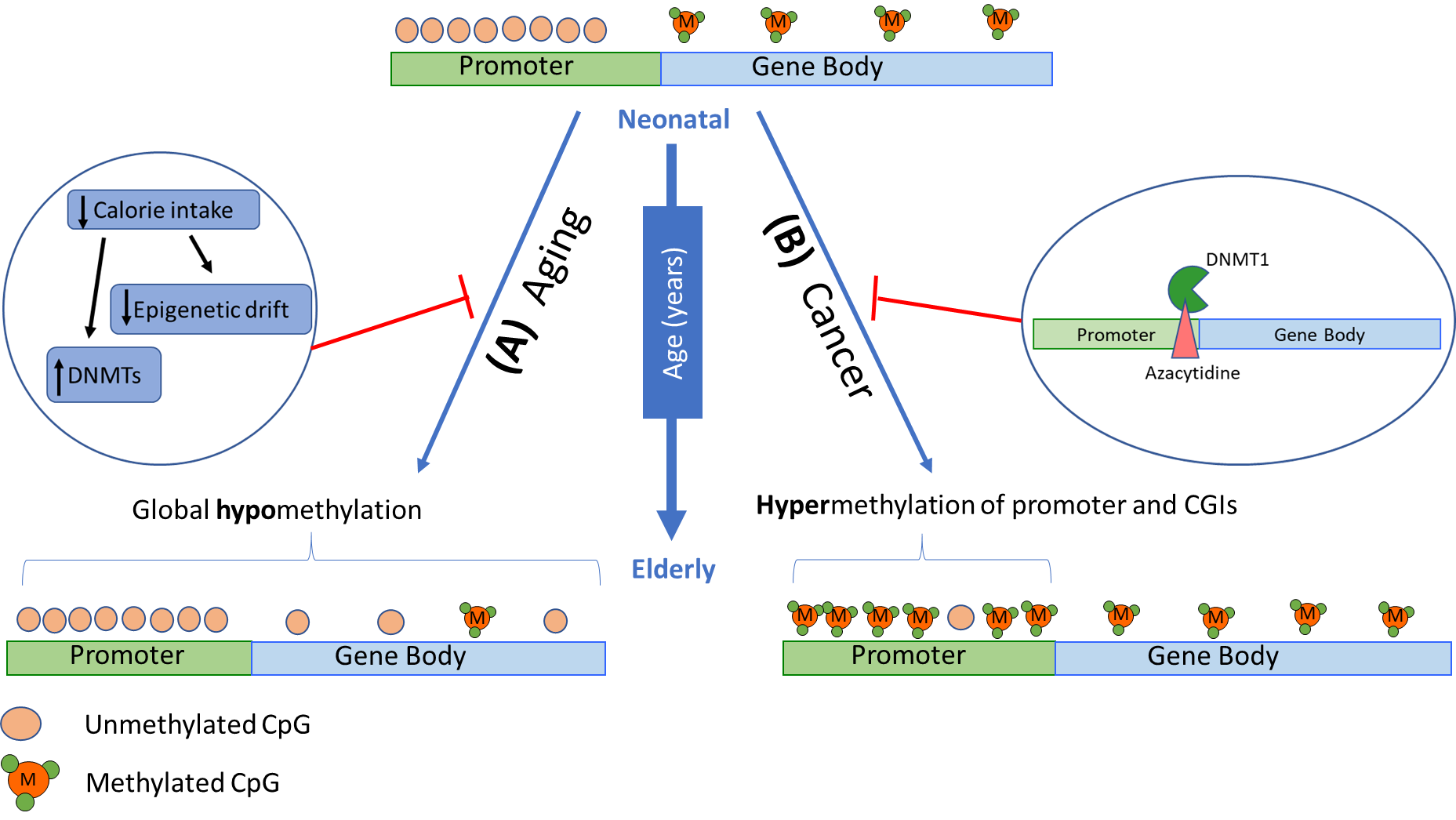
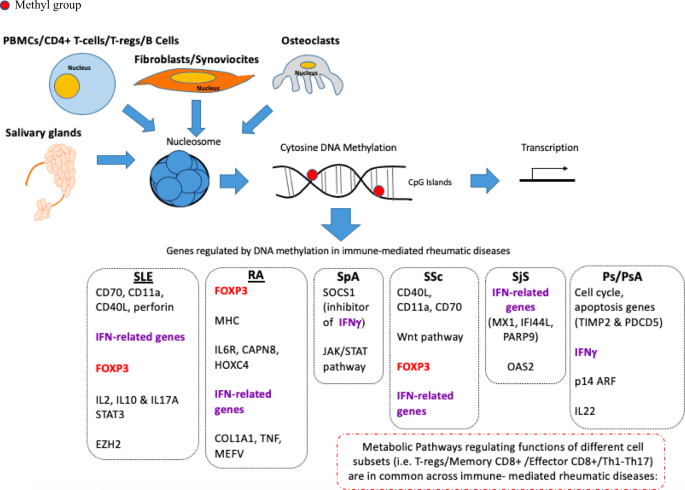
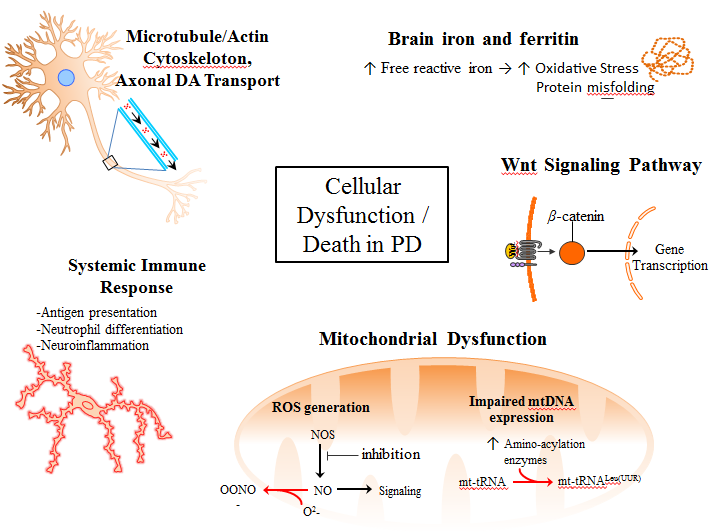
These diseases result from the misregulation. One epigenetic link DNA methylation is potentially an important mechanism underlying these associations. DNA methylation patterns are globally disrupted in cancer with genome-wide hypomethylation and.
Accumulated abnormal DNA methylation during a lifespan is believed to have an impact on the behavior and functionality of stem cells 89. Here we generate and analyse DNA methylomes from highly purified cardiomyocytes of neonatal adult.
DNA methylation patterns are globally disrupted in cancer with genome-wide hypomethylation and.
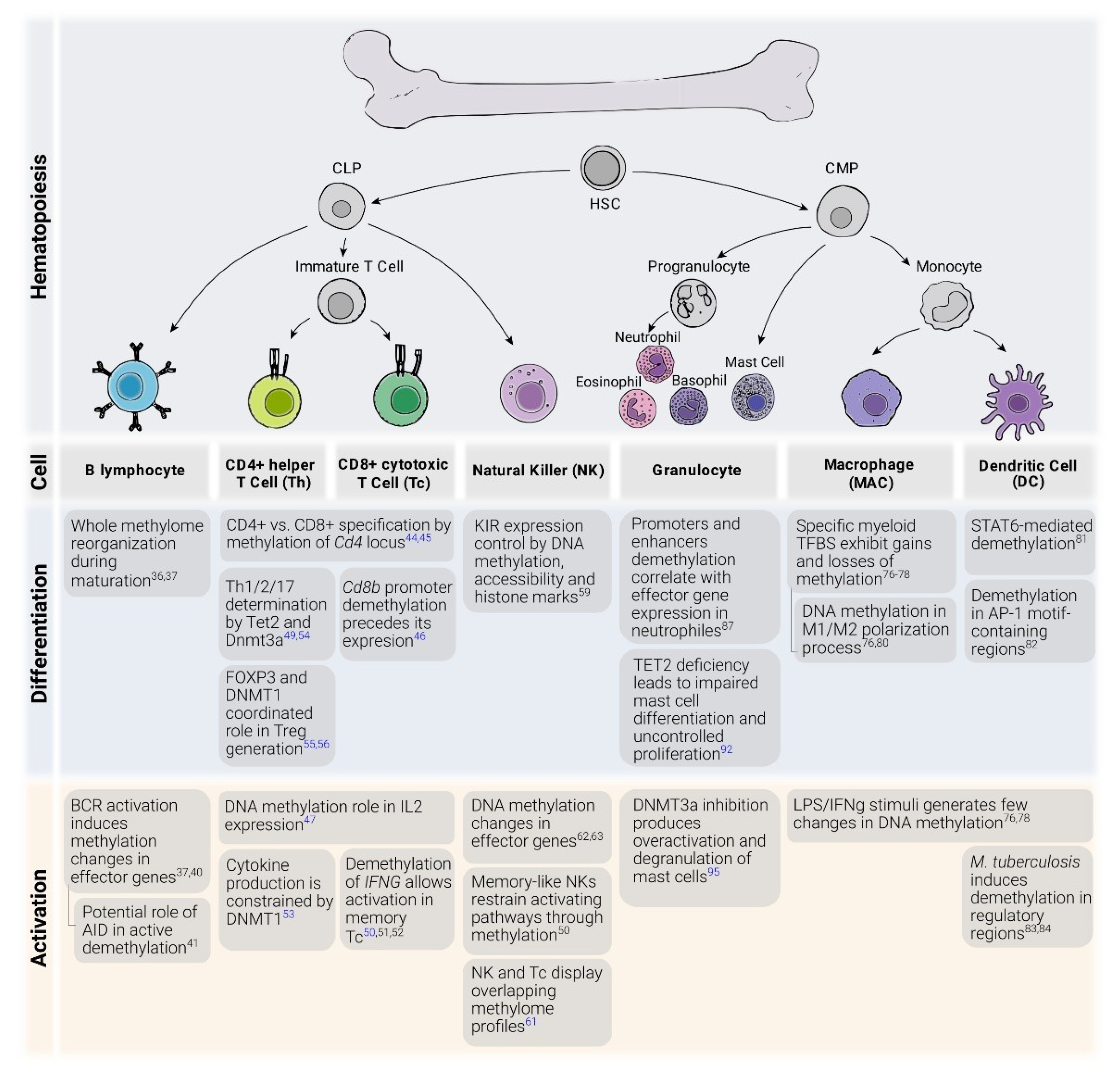
It was shown that DNA methylation and inactivation of myeloerythroid genes protects hematopoietic stem cells HSCs from premature differentiation suggesting a link to tissue homeostasis 90. These include embryonic development transcription chromatin structure X chromosome inactivation genomic imprinting and chromosome stability. DNA methylation is of paramount importance for mammalian embryonic development. Accumulated abnormal DNA methylation during a lifespan is believed to have an impact on the behavior and functionality of stem cells 89. DNA methylation has recently moved to centre stage in the aetiology of human neurodevelopmental syndromes such as the fragile X ICF and Rett syndromes. By inhibiting DNA methylation in a mouse model for intestinal tumors for example it is possible to dramatically decrease the occurrence of adenomas 119 and the same is true for other cancer. DNA methylation present in gene promoters gene bodies and repeated sequences has different effects. DNA methylation has numerous functions. DNA methylation is a complex process that could hold major clues to health and aging but many more large-scale human studies are needed to fully understand its effects.
DNA methylation is of paramount importance for mammalian embryonic development. DNA methylation is a complex process that could hold major clues to health and aging but many more large-scale human studies are needed to fully understand its effects. To improve DNA methylation. DNA methylation is an attractive topic in the study of complex diseases because it may be restored by environmental factors and dietary interventions 18 23. The significance of DNA methylation in shaping the phenotype of the heart remains only partially known. We further identified a DNA methylation signature involving STAT motifs associated with FLT3-ITD mutations. In particular epigenetic changes in psoriasis and atopic dermatitis have been increasingly studied with DNA methylation the most rigorously investigated to date.




























Post a Comment for "Dna Methylation And Disease"