Top Of Basilar Syndrome
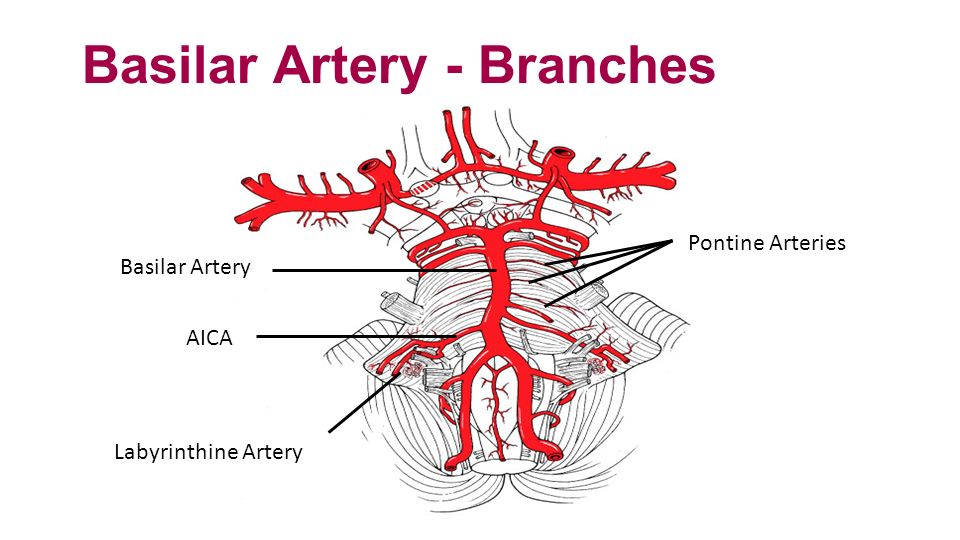
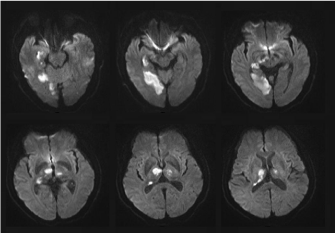
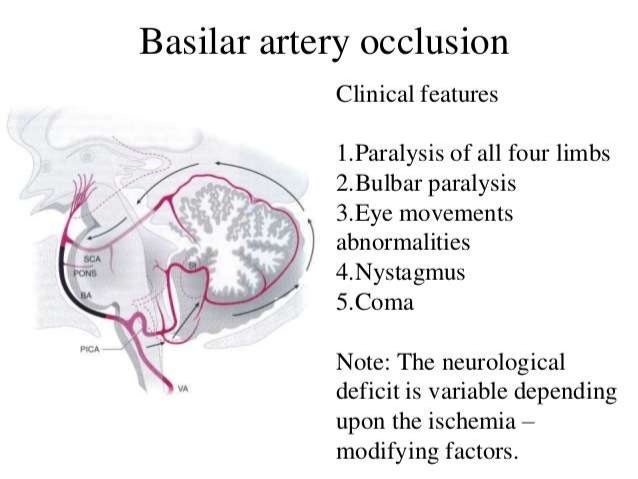
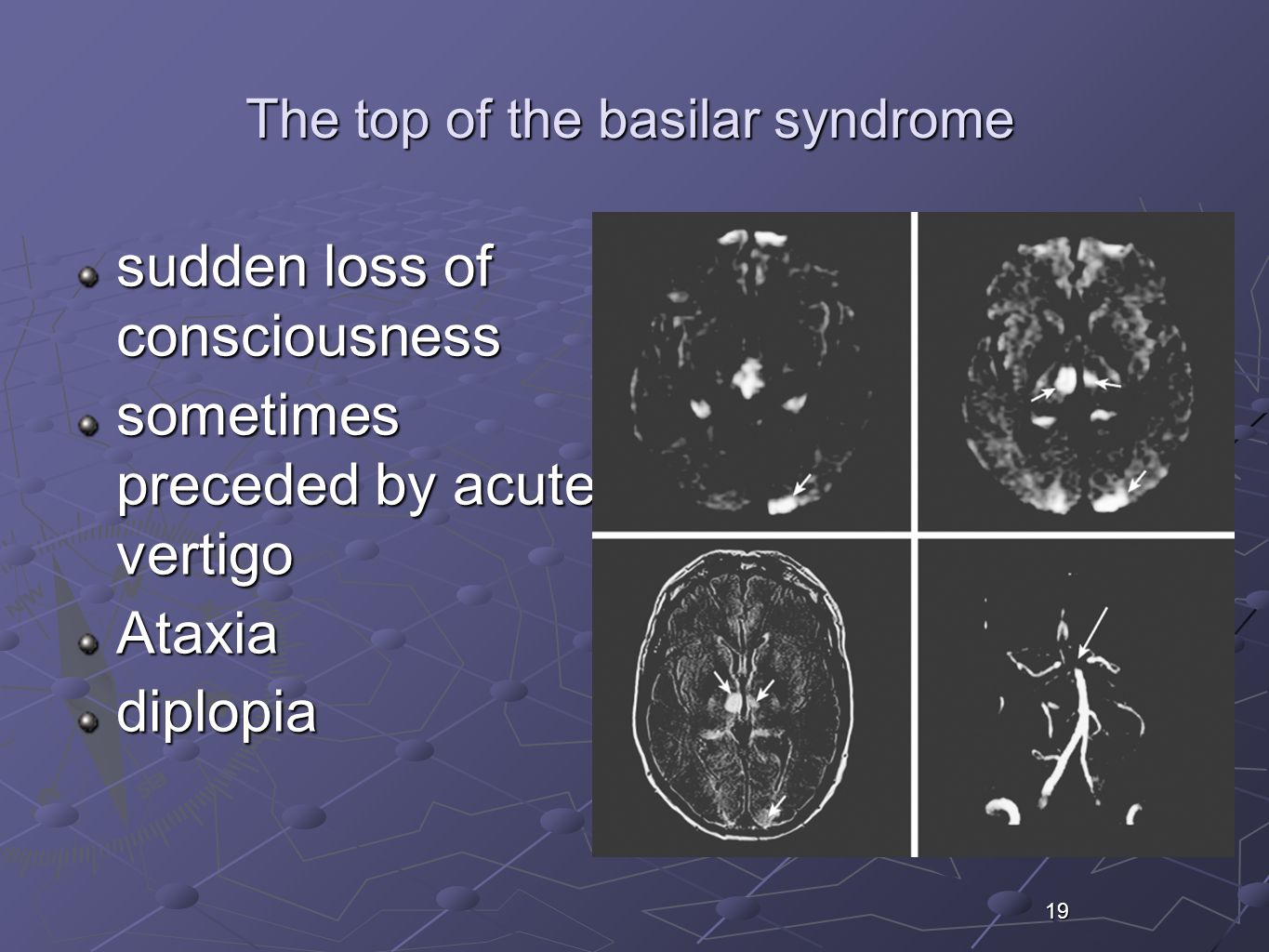
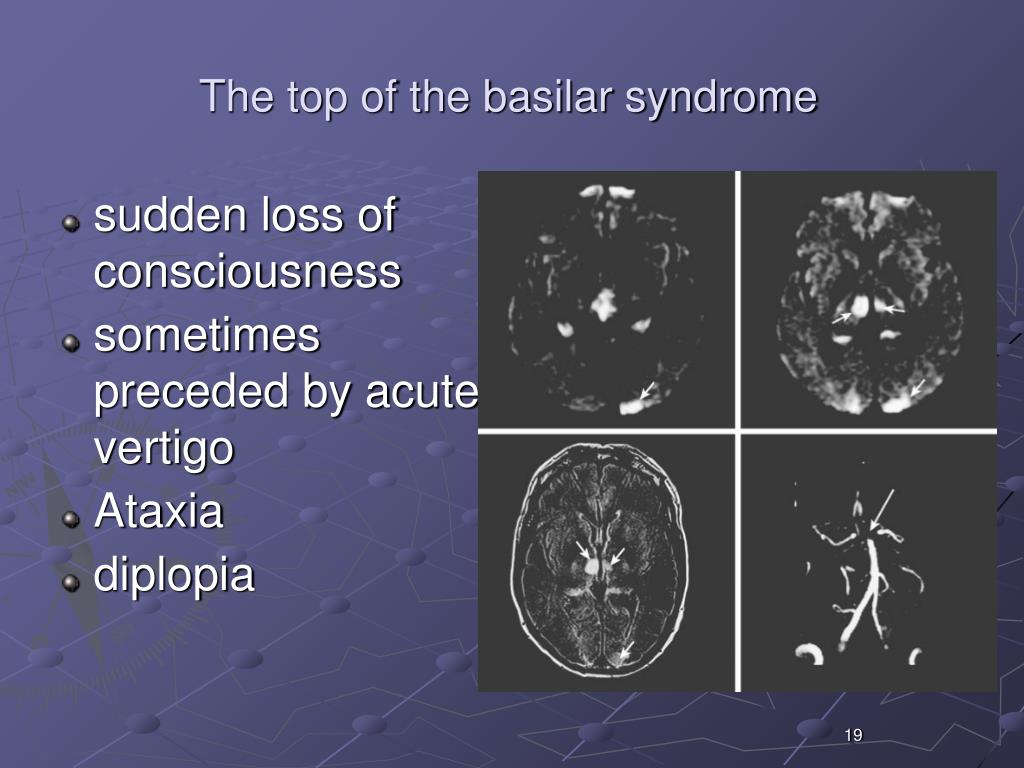
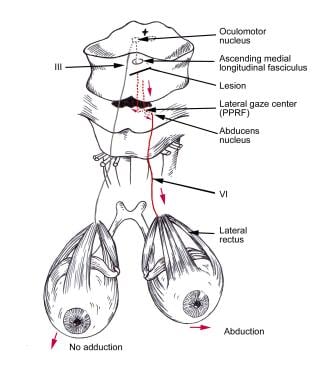
Top of basilar syndrome. Top of the basilar syndrome leads to dizziness vertical gaze and convergence disorders decreased-absent pupillary light reflex hypersomnolence abnormal behavior ataxia dysarthria decreased respiratory drive and coma many of the symptoms that our patient developed. The top of the basilar syndrome is most often due to an embolus. For example a mid-basilar occlusion with bilateral pontine ischemia can cause locked-in syndrome which has a mortality of 758 Occlusions at other regions can cause quadriplegia and cranial nerve III palsy.
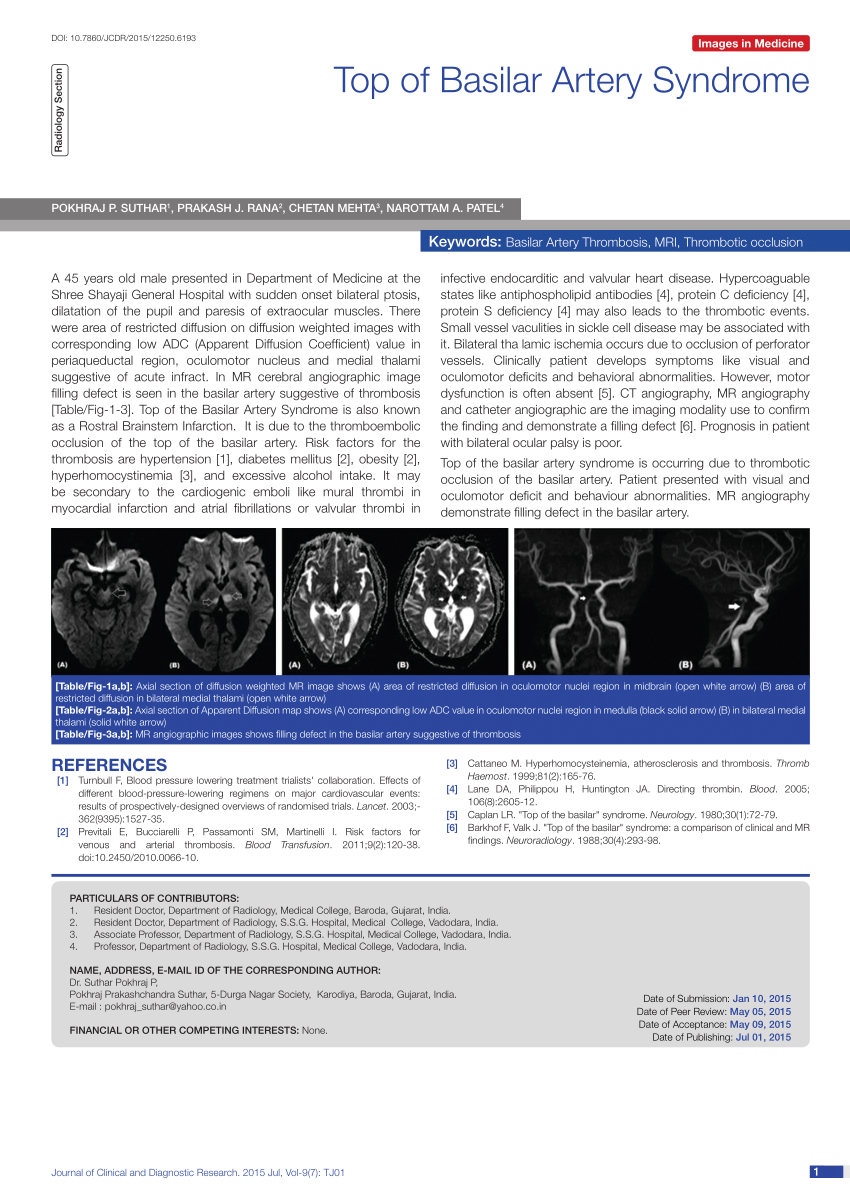
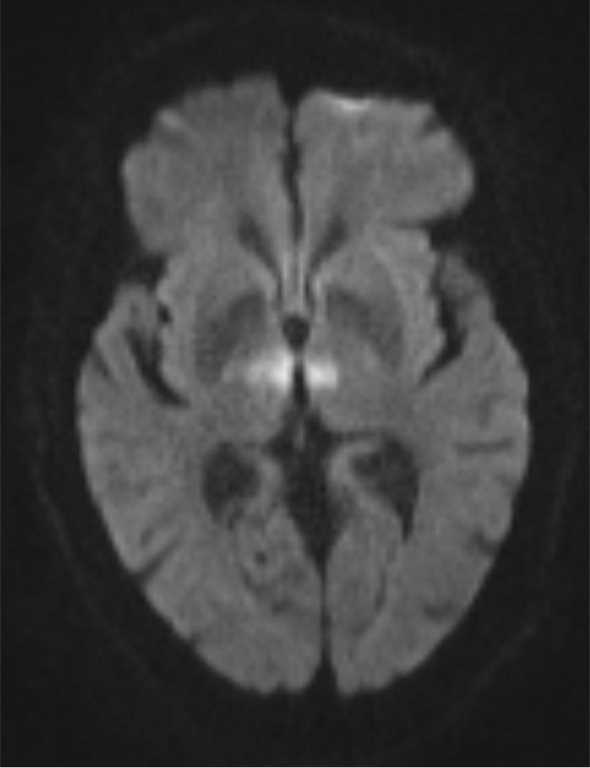
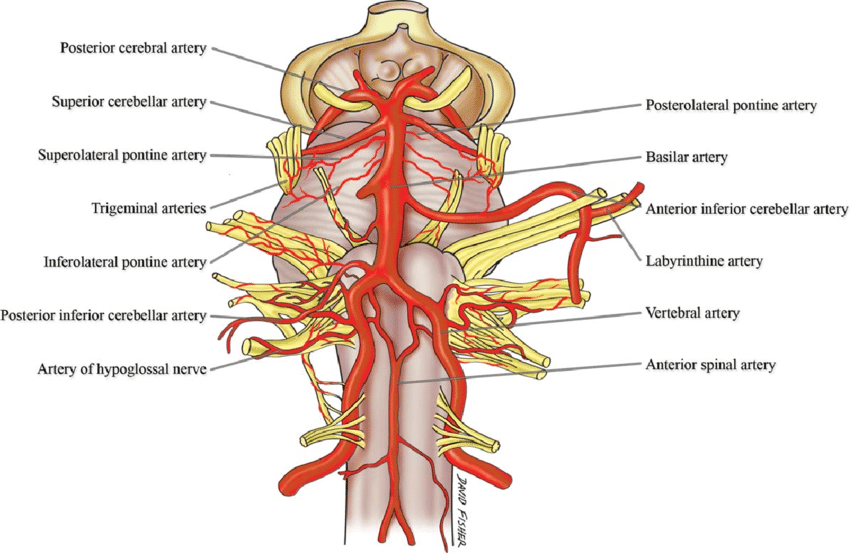
This syndrome is the manifestation of upper brainstem and diencephalic ischemia caused by occlusion of the rostral basilar artery. Clinically top of the basilar syndrome is characterized by. Cranial magnetic resonance imaging seems to be useful for the differential diagnosis of persistent disturbance of consciousness in top of the basilar syndrome.
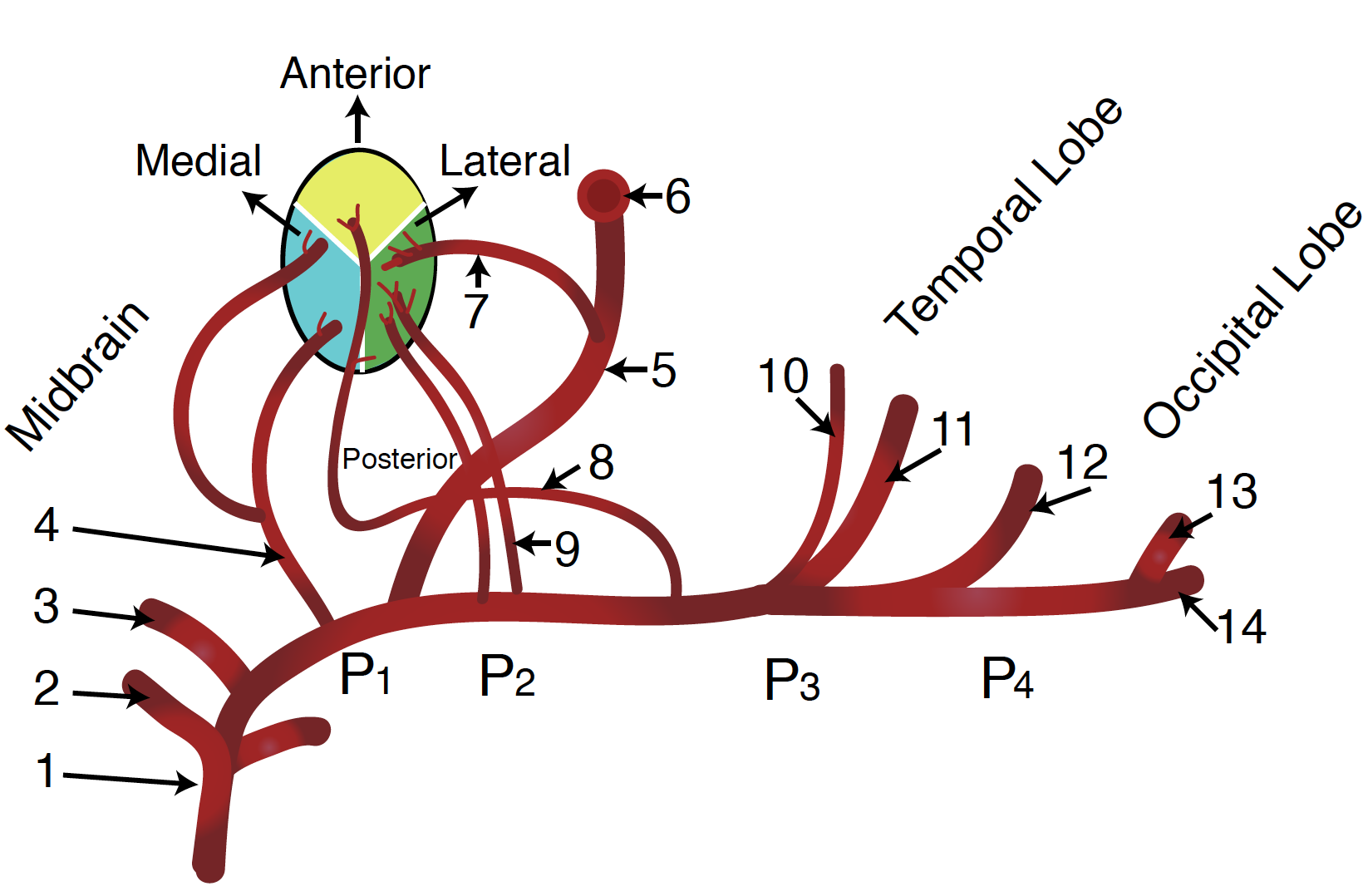
However often clinical symptoms may result due to occlusions of more proximal segments of the basilar artery and its braches especially the posterior cerebral artery. Neurology A condition caused by a lesion of the rostral brainstem characterized by confusion hallucinationspeduncular hallucinosis prominent pupillary abnormalities ptosis and disorder ocular movements. The top of the basilar syndrome is most often due to an embolus.
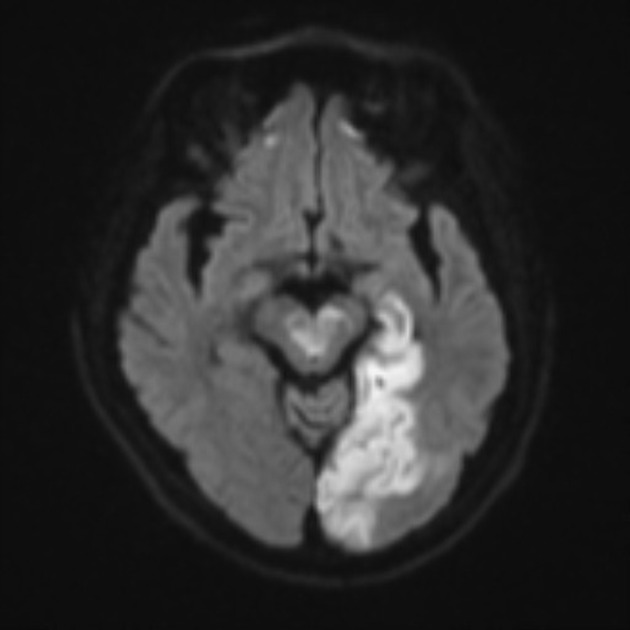
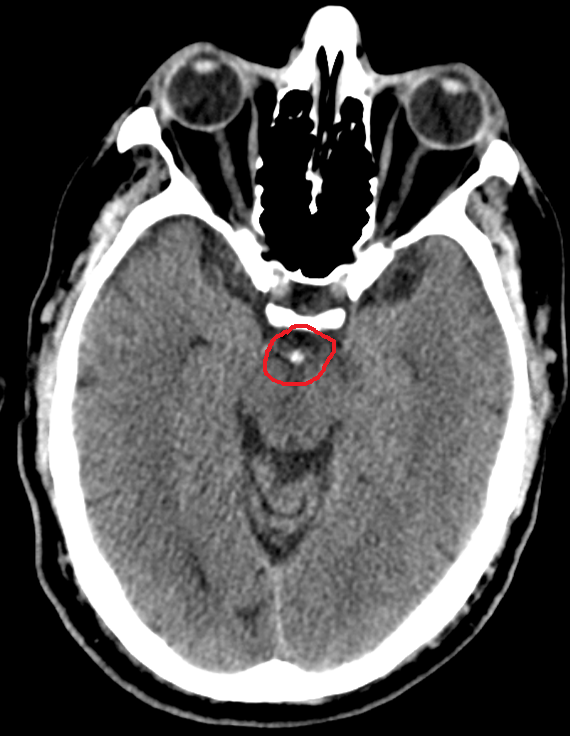
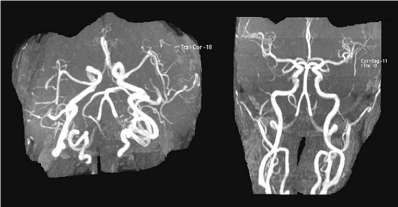
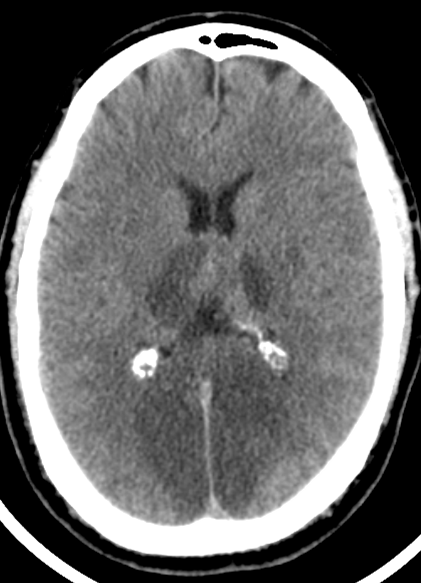
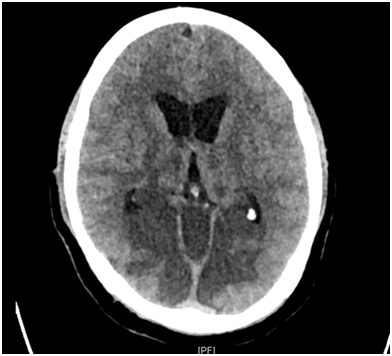
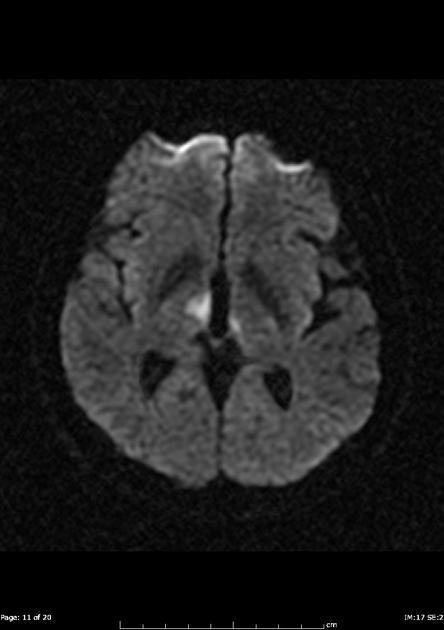
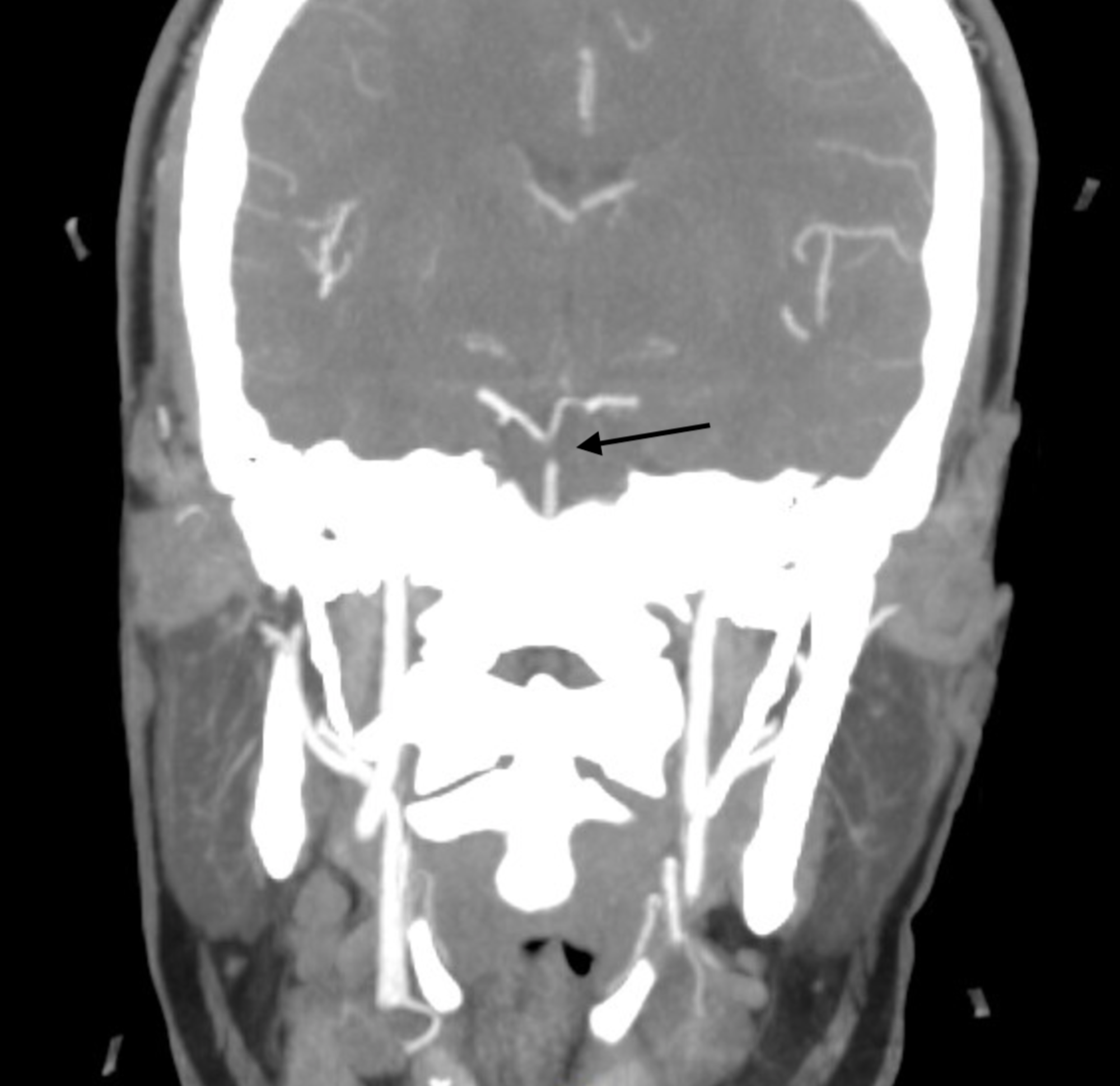
The top of the basilar artery is hyperdense. The top of the basilar syndrome is most often due to an embolus. Discussion Top of basilar artery syndrome may result from atherosclerotic thrombosis of the basilar artery cariac or large vessel emboli vasculitis giant aneurysm involving basilar artery or balloon angiography 1.
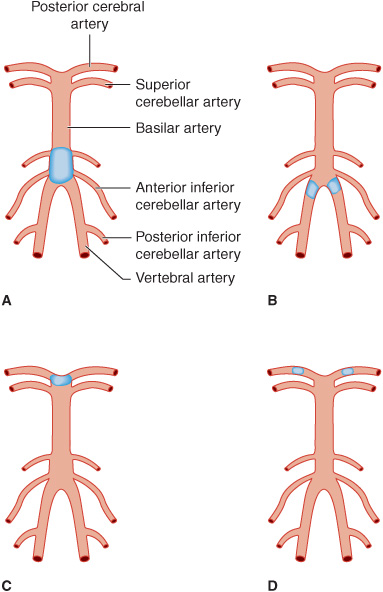
Top of basilar syndrome typically occurs with thromboembolic occlusions of the distal third or tip of the basilar artery. Temporal and occipital infarctions are frequently accompanied by hemianopia with distinctive characteristics fragments of the Balint syndrome amnestic dysfunction and agitated behavior. Occlusive vascular disease of the rostral basilar.
Authors Mohammad Bourmaf 1 Roohi Katyal 1. 72-79 January 1980 rap of the basilar syndrome Louis R. Thus an early diagnosis of BAO is.
The TotBS may be accompanied by somnolence and inattention due to infarction of the rostral mesencephalic reticular formation. On clinical examination the patient may demonstrate visual and.
The top of the basilar artery is hyperdense.
This syndrome is the manifestation of upper brainstem and diencephalic ischemia caused by occlusion of the rostral basilar artery. Discussion Top of basilar artery syndrome may result from atherosclerotic thrombosis of the basilar artery cariac or large vessel emboli vasculitis giant aneurysm involving basilar artery or balloon angiography 1. Temporal and occipital infarctions are frequently accompanied by hemianopia with distinctive characteristics fragments of the Balint syndrome amnestic dysfunction and agitated behavior. Top of Basilar Syndrome Presenting With Hyperekplexia Initially Diagnosed as a Convulsive Status Epilepticus. Occlusive vascular disease of the rostral basilar. The top of the basilar artery is hyperdense. Epub 2020 May 22. 72-79 January 1980 rap of the basilar syndrome Louis R. For example a mid-basilar occlusion with bilateral pontine ischemia can cause locked-in syndrome which has a mortality of 758 Occlusions at other regions can cause quadriplegia and cranial nerve III palsy.
The TotBS may be accompanied by somnolence and inattention due to infarction of the rostral mesencephalic reticular formation. Top of the basilar syndrome. Hemianopia with distinctive characteristics fragments of the Balint syndrome amnestic dysfunction and agitated behavior. The top of the basilar artery is hyperdense. The main symptoms of top of the basilar syndrome are disturbances of consciousness hypersomnia and vertical gaze palsy with quadriplegia being uncommon. Temporal and occipital infarctions are frequently accompanied by hemianopia with distinctive characteristics fragments of the Balint syndrome amnestic dysfunction and agitated behavior. For example a mid-basilar occlusion with bilateral pontine ischemia can cause locked-in syndrome which has a mortality of 758 Occlusions at other regions can cause quadriplegia and cranial nerve III palsy.























Post a Comment for "Top Of Basilar Syndrome"